Hướng Dẫn A-Z, Kiến Thức Wordpress
How to Add a New Post in WordPress and Utilize all Features
Are you trying to create a new post in WordPress? Do you want to learn about all the WordPress post features you see on your screen?
While some may think that adding a new WordPress post is quite self-explanatory, many beginners find the interface a bit overwhelming. Not to mention, sometimes even the more savvy users are surprised to find the hidden gems on the post edit screen.
In this beginner’s guide, we will walk you through all the features on the add new post screen, and how you can utilize them to create better content.

We have divided this guide into three sections to help you easily find what you’re looking for:
- Creating a New Post in WordPress Using The Default Editor
- Adding Images, Videos, & Other Media
- Creating a New Post in WordPress Using The Classic Editor
- Bonus Tips for Creating Better Blog Posts
Ready, let’s get started.
Creating a New Post in WordPress Using The Default Editor
In December 2018, WordPress introduced a new modern block-based editor also known as Gutenberg. It is clean and simple, but don’t let the looks deceive you.
Behind its clean interface, there are tons of powerful features neatly tucked away. We’ll explain all of them and help you unlock their true potential.
Adding Title and Content Blocks
The WordPress block editor comes with a clean writing interface. At the top, you will enter your post’s title.

To add content, you need to add a block.
There are multiple add block buttons on the screen that you can click to select and add a block.

If you don’t want to use a mouse to click on the button, then you can use a keyboard shortcut.
Simply type / to search and add a block.

All content elements are wrapped in a block. WordPress comes with blocks for all the common content items, including paragraphs, columns, images, galleries, shortcodes, embeds, widgets, and more.
Some WordPress plugins may also add their own blocks to add other features like contact forms, SEO, etc (more on this later in the article).
Adding Images, Videos, & Other Media
You can add images by simply adding the image block and then uploading or selecting the image you want to add.

If you want to text and image next to each other, then you can use the ‘Media & Text’ block.
This block helps you wrap text around the image in WordPress.

WordPress editor also comes with a Gallery block that you can use to display images in rows and columns with a grid layout.
Simply add the Gallery block and then upload or select the images from your WordPress media library.

While the gallery block is powerful, you may need other advanced gallery features like albums, image sorting, etc. In that case, we recommend using one of these WordPress gallery plugins.
Want to embed a video in your content? No problem.
The default WordPress editor comes with embed blocks for all popular providers.

You can also just copy and paste the video URL to a paragraph block.
WordPress will automatically convert it into a video embed block.

While you use the video block to upload videos directly to your website, we recommend against that because it will slow down your website and can even crash your WordPress hosting server.
Instead, we recommend uploading your videos on a service like YouTube or Vimeo, and then embedding it in your WordPress posts.
For more details, see our guide on why you should never upload videos to your WordPress site.
Adding Categories and Tags
WordPress allows you to sort your posts into categories and tags. These taxonomies help you organize your content into sections and topics.
They also help with WordPress SEO and make it easier for your users to find the content they are looking for.
The categories and tags meta boxes are located in the right-hand column.

Adding Featured Image
A featured image (also known as a post thumbnail) is the main article image that represents the content. They’re prominently displayed on your website on single posts, blog archive pages, as well as on the homepage of news, magazine, and blog websites.
Almost all WordPress themes support the featured image functionality. You will find the option to add a featured image to your post in the right column.

Simply click on the ‘Set featured image’ button and then select or upload the image you want to be used as the featured image.
It’s important that you don’t confuse featured images with cover images which is a new feature. See our article on cover image vs featured image for more details.
Adding Excerpts (Article Summary)
Excerpts are the summary of a blog post or article. Most WordPress themes can automatically generate the excerpt from the first few lines of your post.
However, this automatic excerpt may not always be meaningful or catchy. In that case, you may want to manually add an excerpt.
You can do so by adding it in the excerpt box located under the Settings column on the right.

Changing Post URL Slug or Permalink
By default, WordPress uses SEO-friendly URLs for your blog posts. It automatically uses your post’s title as the permalink.
However, some users may want to change it to be more SEO and user-friendly. There are two ways to do that.
You can click on the post title, and you’ll notice the option to change the permalink above the title field. Alternatively, you can change it from the Permalink tab under the Settings column.

Changing Author
If you run a multi-author WordPress site, then you can also change a post’s author and assign it to a different author on your website.
You will find the option to change author under Settings in the right column.

Turn Comments On / Off
WordPress comes with a built-in commenting system that allows users to leave comments on your post.
You can turn off comments for individual posts from the Discussion tab. Simply uncheck the ‘Allow comments’ option.

You’ll also see the option to allow pingbacks and trackbacks. These allow you and other blogs to notify each other when they link to an article.
However, it is mostly used for spam, so we recommend completely disabling pingbacks and trackbacks.
Options Added by WordPress Plugins
Most popular WordPress plugins will also add their own options to the post edit screen. Some will be available as blocks while others will be available as meta boxes.
For example, WPForms, the best WordPress contact form plugin adds a block to insert contact forms in your posts and pages.

Another great example would be All in One SEO (AIOSEO). They add a meta box below the editor for SEO settings and another one in the top toolbar.
You read our full guide on how to setup All in One SEO for WordPress for more details.

Publishing Options
The default WordPress edit screen is divided into two columns. The left column is where you write content, and the right column has all post settings including publishing options.
Let’s take a look at publishing options in the right column.

- The ‘Save’ button allows you to quickly save changes you made to a WordPress post. The editor will also automatically save your changes as you write.
- The preview button will open a live preview of your post or page in a new browser tab.
- Once you are done editing your post, you can click on the Publish button to make your post go live.
- WordPress gives you a few options to control the visibility of your post. The default option is ‘Public’ but clicking on it will show you options to make a post private or password protected.

- WordPress also allows you to control when a post is published. The default option is to publish immediately, but you can also schedule your posts to publish later or even select a past date.
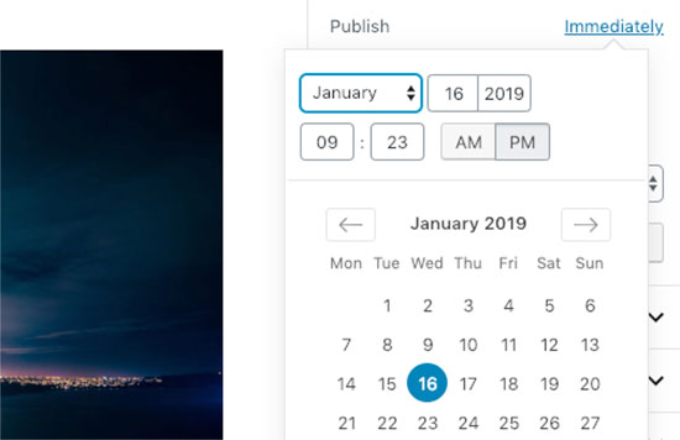
- Checking the box next to ‘Stick to front page’ will make a post sticky or featured. This makes the specific post appear on top of other posts.
- Pending review option will add a custom status next to your post as ‘Pending review’. This feature is particularly helpful on multi-author blogs where contributors can just save posts and not publish them.
- If you want to delete a post, then you can click on the ‘Move to trash’ button. WordPress will send the post to the trash. Deleted posts will remain in the trash folder for up to 30 days. After that, they will be deleted permanently.

Edit Screen Options
WordPress allows you to show and hide panels from the edit screen.
You can do so by clicking on the three-dot menu at the top-right corner of the screen and then clicking on the ‘Options’ button.

This will bring up a popup.
Here, you can check or uncheck the panels you’d like to view.

Other Post Edit Screen Options
There are many other options on the post edit screen. Most of them are related to the appearance of the post edit screen and the editor itself.
Let’s explore them.
When you click on the three-dot menu icon at the top right corner of the screen, you will see options to move block toolbar to the top, spotlight mode, fullscreen mode, switch between visual editor or code editor, manage reusable blocks, and keyboard shortcuts.

Next to it, you will see a button with the gear icon.
Clicking on it will show/hide the block settings column.

On the top-left corner of the screen, there are a few more buttons.
First, from the right, you will see the block navigation button which allows you to quickly jump to a block in your post.

Next, you will see the information icon.
Clicking on it will show you post stats like the number of words, paragraphs, headings, and blocks.

After that, you have Undo and Redo buttons
They allow you to undo changes you made to your posts before saving or publishing them.

Finally, you have the add block button which allows you to insert blocks to the post editor.
The default WordPress editor is quite powerful.
We encourage you to explore it on your own when writing blog posts and pay attention to the individual block settings. Each block has different settings, and you’ll discover a lot of neat tricks there.
Creating a New Post in WordPress Using The Classic Editor
If you are still using the old classic WordPress editor, then this section is for you.
The classic editor will be supported until the end of 2021, and we strongly recommend all users to create a plan for switching to the new WordPress editor.
Title and Content Boxes
In the classic editor, title and content boxes are the most noticeable areas on the Add New Post screen (see the screenshot below).

Yours might look slightly different depending on whether you are using the visual or the text editor.
You can switch between visual and a text editor while writing a post, but we do not recommend switching as this could mess up your post’s formatting.
Visual Editor is a beginner-friendly text editor with formatting buttons and a nice visual layout for the content area. On the other hand, the text editor is a plain text editor where you can actually see the HTML or write your own.
The first text area on the top is where you add the post title. If you are using SEO Friendly URL structure, then WordPress will auto-generate the post URL based on your title. You can edit the URL by clicking on the edit button.
The content area is where you will write your post. You can use the formatting options from the toolbar or use one of the many keyboard shortcuts available which will speed up your writing process.
If you are using the visual editor, then you may want to take a look at these tips for mastering the WordPress visual editor.
In the footer area of the content editor, WordPress will show you the word count for your post. This is especially useful if you’re writing a guest post or an article that needs to meet a certain number of words.
As you write, WordPress will automatically save a draft of your post. This autosave is stored in your WordPress database temporarily.
As soon as you save your draft or write more content, WordPress cleans up your autosave temporary draft and replaces it with a new one. This process ensures that you do not lose your content due to an internet connection or hardware failure. See our guide on how to undo changes in WordPress with post revisions.
The post editor shows your current draft and autosave status in the footer next to the word count.
Add Images and Media
Between the title and content fields, there is a large Add Media button. You will need to click on it when you want to upload an image or any other media to your WordPress post. This will launch the media uploader in a popup window.

Simply click on the select files button to upload images or any other media to your WordPress site. You can also create image galleries from uploaded files.
WordPress comes with some basic image editing tools. See our tutorial on how to edit, flip, rotate, and crop images in WordPress.
Publishing Options
The WordPress post edit screen is divided into two columns. The column on your left contains the post title and content editor. On your right-hand side, you have different meta boxes to configure post settings.
The top meta box in this column is labeled Publish. This is where all the publishing options for your posts are managed.

1. Save Draft button stores a draft of the post or page that you are working on. WordPress also auto-saves your posts as you write them.
2. Preview button shows a live preview of your post. You can use it to see how your post will look after publishing.
3. Status allows you to set a status for your post. WordPress automatically handles post status for drafts and published posts. Unless you are using a plugin to add custom statuses, you don’t need to worry about this option.
4. Click on the Edit link next to visibility to expand it. The first option under visibility will allow you to make your post sticky on front-page. Sticky posts in WordPress are like featured content that are displayed on top of all other posts.
5. The next option allows you to password protect a post in WordPress.
6. The third option under visibility is labeled private. This allows you to privately publish a post on your WordPress site. The private posts will be visible to users who have the editing privileges on your site.
7. Click on the edit link next to Publish, and WordPress will display the time and date options. You can use this option to schedule posts or create back dated post in WordPress.
8. Move to trash allows you to delete a WordPress post. Deleted posts live under trash, and you can restore them if you need to for up to 30 days.
9. Finally, the publish button makes your WordPress post public. Remember if you scheduled a post, then it will appear on your site on the scheduled date and time.
Adding Categories and Tags
You can sort your posts into categories and tags. The categories and tags meta boxes usually appear in the right-hand column below publish meta box.

Categories and tags help you organize your content in a meaningful and browsable format.
Not only does it help users easily find your content, but it also boosts your site’s SEO. See our guide on the difference between categories and tags and how to use them to sort your content.
Featured Image (Post Thumbnails)
Most WordPress themes support featured images or post thumbnails for articles. Usually, it is the last box in the right column on your post edit screen.

Simply click on the set featured image link, and it will bring up the media uploader popup. You can select an image from your previous uploads or upload a new image from your computer.
For more detailed instructions, see our guide on how to add featured image or post thumbnails in WordPress.
Screen Options
Some of the options on the post edit screen are hidden by default to present a cleaner and simpler editing experience. These options are not commonly used by beginners. However, you may need them later.
Simply click on the Screen Options button on the top right corner of the page. This will show a menu with checkboxes next to option names.

As you can see some of the options will already be checked. For the others, you can display them by clicking on the checkbox next to an option name, and it will appear on your post edit page.
Let’s take a look at some of these options and what they do.
Excerpts
Checking this box adds a meta box below your content editor. You can use this box to add a short summary or excerpt for your post.

Ideally, you should display a summary or excerpt for your posts on your site’s front page and archives. Full content should only be displayed on the post’s single page.
Learn more about this in our guide full post vs summary (excerpt) in your WordPress archive pages.
Send Trackbacks
Send Trackbacks option allows you to notify other blog owners that you have linked to their content.

If the other blog owner is running WordPress, then you don’t need to send them trackbacks. Your WordPress site will automatically send them a ping when you publish the post.
Trackback feature is misused by spammers so much that many site owners simply disable them. We have an article on dealing with trackback spam in WordPress.
Custom Fields
This option will display a user interface for custom fields below your post editor. You can use it to manually enter custom information in your posts. See our WordPress custom fields 101 guide for beginners to learn more.

Discussion
While comments are a great way to engage your audience, sometimes you may not want to have comments on a specific post or a page.
The discussion option displays a meta box below the post editor to turn on/off comments and pingbacks for your post.

Since pages are supposed to be like static pages, most users want to turn off comments on them. You can do so by editing each page, or you can see this tutorial to turn off/disable comments on WordPress pages.
Once your WordPress site gets some reputation, you will start getting an increase of comment spam. Instead of turning off comments, you may want to try these tips and tools to combat comment spam in WordPress.
Slug
A slug is a cleaner title that can be used in URLs.
http://example.com/2015/07/this-is-post-slug
WordPress automatically generates a post slug and displays it as the post URL just below the post title. You can edit the URL slug by clicking on the edit link below the post title.
You can also enable the slug option from the Screen Options and edit your post slug there.

Author
WordPress will automatically assign you as the post author when you create a post.
However, sometimes you may want to show another user on your WordPress site as the author. Enabling the author checkbox allows you to do that from the post edit screen.

Bonus Tips for Creating Better Blog Posts
The reason why WordPress is the most popular blogging platform is because it comes with a great set of tools right out of the box to help you create new content.
However, there are many other tools and tips that you can use to improve your blog content.
The first tip we offer to everyone who’s just starting a blog is consistency. Make sure that you regularly publish blog posts. You can plan an editorial calendar and then stick to it.
We recommend starting with 1 – 2 posts a week and then gradually increasing your pace.
Often new users struggle with finding post ideas for their blog. Here is a massive list of blog post ideas that you can use to get started. You can also use WPBeginner’s free blog post idea generator to get 250+ new ideas instantly.
You’ll also need to learn how to promote your posts and keep track of things. Our team has picked the best content marketing tools that will help you grow your blog.
Lastly, you can optimize your website for search engines like Google. This is where AIOSEO comes in handy, as it helps with search engine optimization (SEO) without any technical knowledge. You can rank for different keywords and drive organic traffic to your blog.
Often users ask us what’s the difference between posts vs pages, and which one is better for SEO? The simple answer is that it depends. Posts are timely content organized in a reverse chronological order which is why they’re called blog posts.
Pages on the other hand are static content such as your about page, contact page, etc. The process of adding a new post or page in WordPress is exactly the same.
For more details, see our guide on post vs pages in WordPress.
We hope this article helped you learn how to add a new post in WordPress like a pro. You may also want to see our essential WordPress SEO guide for and the best email marketing services for small businesses.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.

